Insights
Perform a Comprehensive On-Page SEO Site Audit
Most small business owners start out by wearing many hats (oftentimes…all the hats). As a business grows, each of those hats will go to a new hire or an agency but having worn that hat, in the beginning, will make life much easier down the road when work needs to be delegated. When it comes to SEO, oftentimes business owners can feel overwhelmed when speaking to their marketing agency or “website guy” handling the work. In this post, we’ll go over how to do a comprehensive On-Page SEO audit of your website. Understanding this now will help sharpen your eye for SEO best practices for your site as it stands today, and also ensure you understand improvements that will be made down the line once the work is offloaded to a professional.
Before we get started, what is “On-Page SEO” and why is it important?
There are 6 main tenets of SEO: On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, Local SEO, Technical SEO, Content Marketing, and UX Design (User Experience). For the purposes of this post, we’re going to focus on the first and most basic tenet, On-Page SEO. Be on the lookout for future blog posts that touch on the other 5. If you are currently working with an SEO Agency or SEO Specialist (or if you are looking to hire one) it is important that you know which of these areas they will be working on. Ideally, you’ll want to make sure all are being taken care of because all 6 tenets of SEO work in tandem; if one is lacking, none are going to be at their full strength.
On-Page SEO is essentially all of the SEO best practices that take place on a page of your site. This involves strategically placing relevant keywords in page titles, headings, content, and meta descriptions. It also includes optimizing images, improving page load speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, and creating a clear URL structure. On-Page SEO ensures that your website’s content and structure are well-aligned with search engine algorithms and user expectations. If every page of your site has great On-Page SEO, your site as a whole will provide a solid foundation to build on for the other 5 tenets of SEO.
Step 1: Keyword Research
It goes without saying that before you get started, you need to do a little research and come up with a solid strategy. Keyword Research is a big job in the beginning but gets easier over time. For now, you’re going to make decisions regarding the keywords you care about and which ones are going to be the most helpful for your brand. This list will be monitored and added to over time as you find more keywords, discover some that you have outgrown, etc.
To make this work easy, we recommend creating an account on Semrush so you can use their keyword manager.
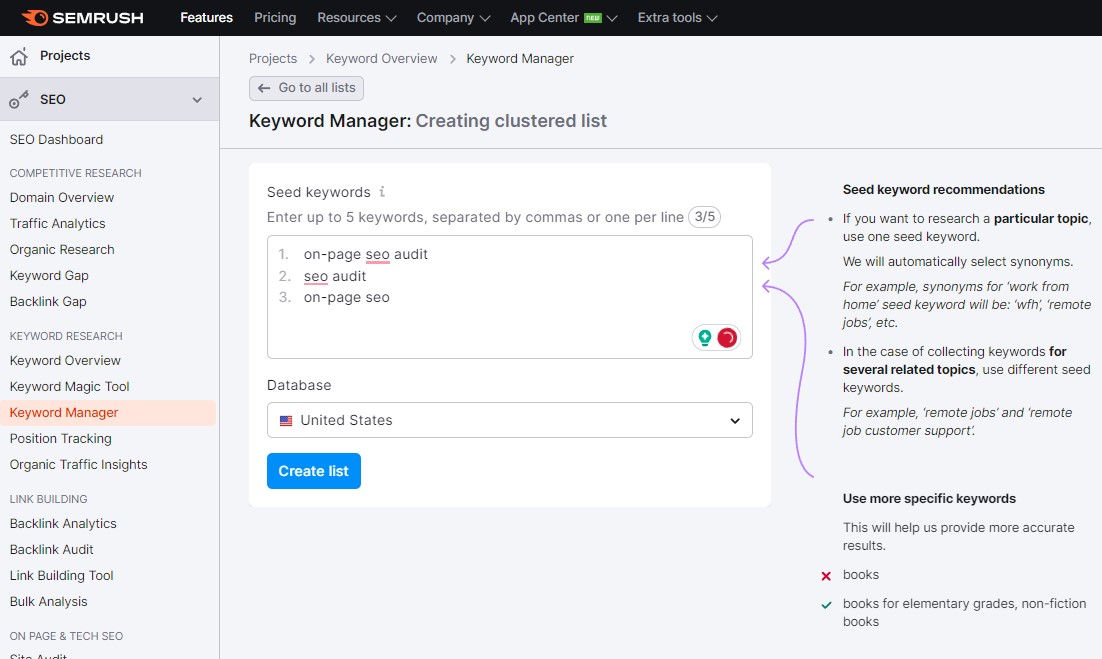
Even a free account with limited access will be enough to get you started. As you discover keywords you think make sense, check their search volume and keyword difficulty (competition) and consider that as part of your strategy. After entering in your desired keywords, the Keyword Manager tool will provide you with keyword clusters to choose from.
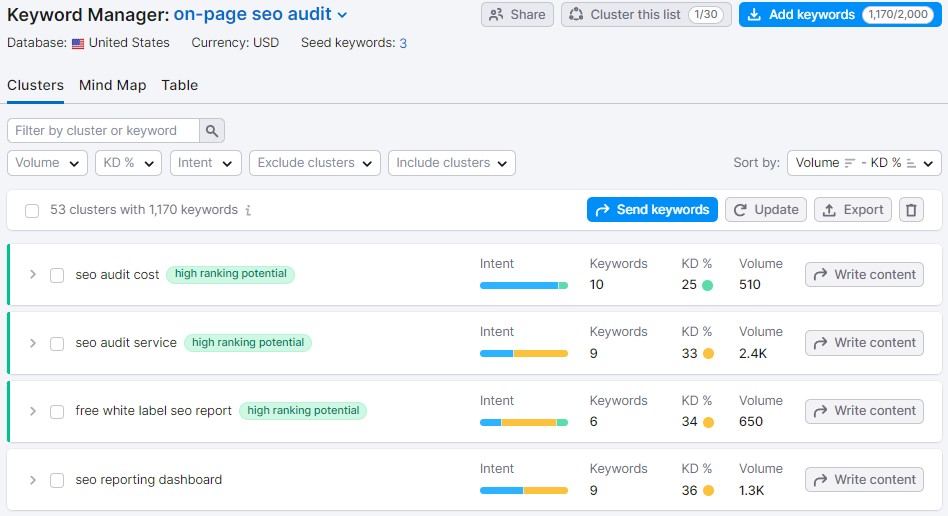
By expanding those keyword clusters, you will be able to see what websites you are competing with for those coveted top organic search results.
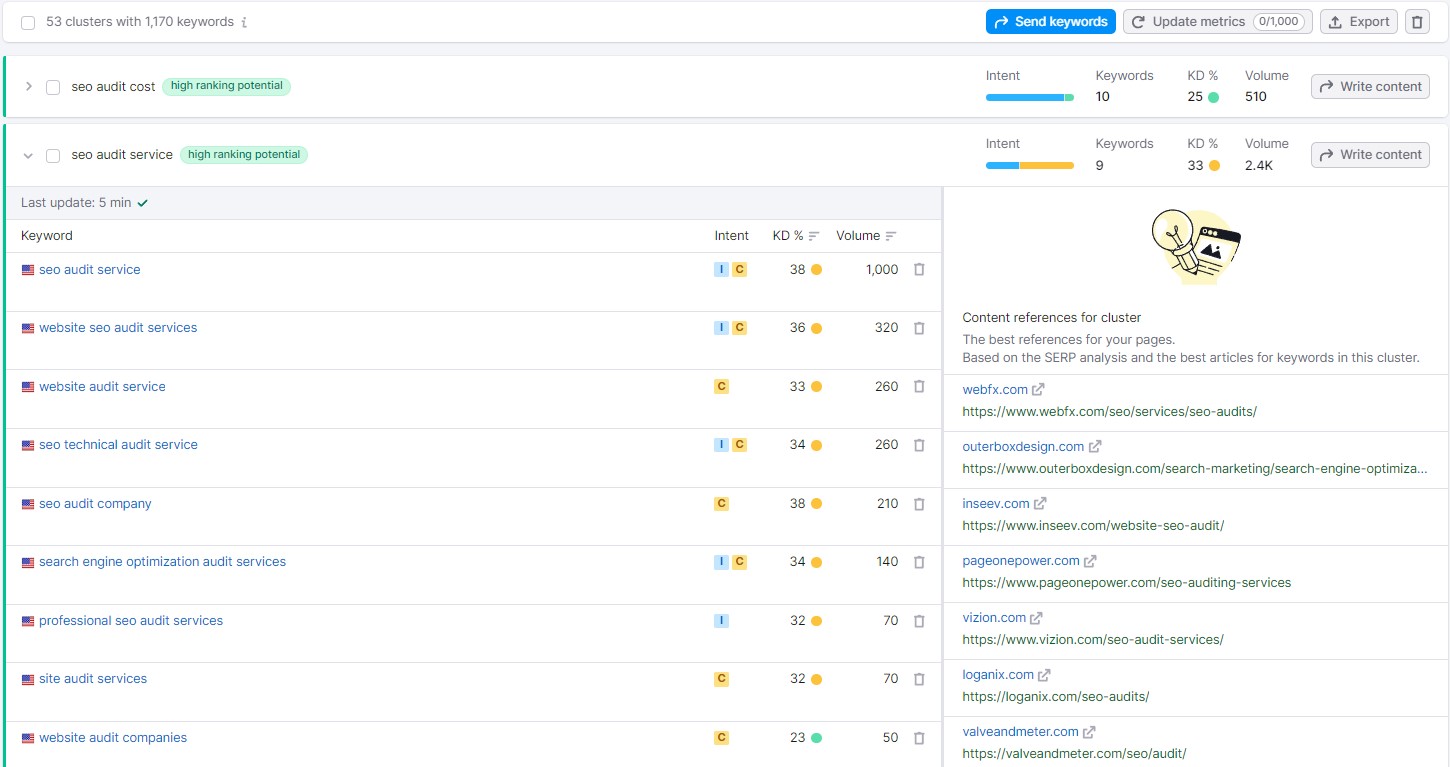
Your next step is to assign a “core keyword” to each page of your site. Now you see why people hire out for this work, it’s step 1 and we’re already getting into the nitty gritty. Yes, you are assigning a core keyword to each page of your site, not to your site as a whole. The reason for this is simple: if you have a page dedicated to an important keyword (let’s say one of your services) and a user types in that keyword, they are more likely to find the answer they are looking for on the services page dedicated to that topic, not on your homepage. Each page of your site should have its own core keyword.
Step 2: High-Quality Content
It should go without saying that the quality of your content matters. Whether it is content on your homepage, services page, or blog page, the acronym Google wants you to know is EEAT. EEAT Stands for Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust. All the content on your website should be written with EEAT in mind. Provide users with a good experience and useful information from a trustworthy, authoritative source. While SEO is all about getting keywords ranked higher on Google, the primary focus of Google is to provide a positive experience to its users. With that in mind, remember that you should be providing users with helpful, reliable, people-first content.
An important facet of having high-quality content is keeping content FRESH. This is a loaded word, and will likely require its own post in the future. The skinny of it is this: don’t let your content become outdated! Update your content, and keep it current. That includes the links, the images, and of course, the information itself. You’ll often hear SEO Experts (us included) say that SEO work is neverending. That is the truth – there is no such thing as completing the optimizations on a website. There is always more that can be done.
Step 3: Keyword Placement
Now that you’ve chosen a core keyword for each page, it’s time to ensure that keyword is in the most effective areas of that page. Here is a checklist for you to go through:
- Page Title
- Title Tag
- Introduction (first 100 words on the page)
- H2 Headings
- Image Filenames (you read that correctly, the filenames matter)
- Image Alt Text (if it fits organically, don’t forget these are first and foremost used for accessibility)
- Meta Description (while these are not a ranking factor, they are pivotal to getting clicks when the page appears in search results)
- Anywhere the keyword fits throughout the page organically (do not keyword stuff/force it)
Before moving on to step 3, it is important to touch on some of the warnings above. The first one being the alt text. Lack of accessibility on the internet is a problem that sees a growing number of lawsuits every year. Alt text is just ONE of the many accessibility requirements of a website and while YES you can use them for SEO purposes, you should only do it if it makes sense. Alt text is used to explain an image to those who cannot see it. If you want to use your core keyword in alt text (you do, trust us) then make sure to use an image that allows you do to that organically. In that same vein, the warning on number 8 about keyword stuffing follows a similar sentiment. Do not use a keyword 10 times just because you can. Use it where it makes the most sense. Keyword stuffing is a confirmed negative ranking factor and something to avoid.
Step 4: Optimize Titles & Headers
There are two titles for every webpage: the Title Tag & the H1 Tag. Most of the time, these are the same because when you create a page and add a title, your CMS will automatically add your page title to the top of the page with an H1 tag attached to it. This is because you should never have more than one H1 tag on a page. That said, you can change your H1 to something different if you would like to have a little more control.
- What is a title tag? A title tag is the title of your webpage. This is sometimes referred to as a meta title, SEO title, or page title depending on what platform you are using. The title tag will appear in 2 places: search results that display the webpage (as pictured below) and the tab of your web browser.
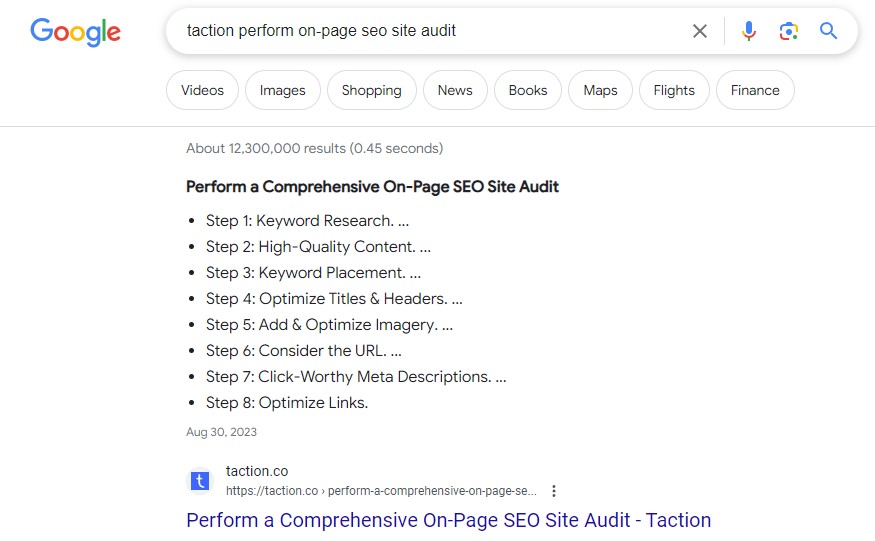
- What is an H1 tag? An H1 tag is the title that users will see on your page. It’s typically the largest text on a page (such as the title of the blog post on this page)
While the H1 tag is the most important of the header tags, there are also H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6 tags. There is no limit to the amount of H2-H6 tags you can use on a page. Following the best practices below will ensure you are using them in a way that adds structure to your site and puts you in a position to rank well with target keywords. While using a plethora of header tags won’t come into play on most pages, it is common practice for blog posts.
Title Tag Best Practices
When a user types in a search query, the search engine will then look through every page it has crawled to provide the user with an answer as fast as possible. When searching for an answer, the title tags are the first on-page metric to be considered.
- ONE Title Tag (H1) on each page (having multiple would be like having a book with multiple titles – confusing)
- Less than 60 characters (or, more specifically, 580 pixels)
- Start with the core keyword, if possible
- Keep it simple and concise
Header Tag Best Practices
When search engines crawl your site, they’ll essentially organize all of the information on your site into an easy-to-read outline. The Site Title will be at the top of the outline followed by the H1 (Title Tag) for each page. By using H2-H6 tags effectively, you can control how search engines organize and dissect the information provided by your website.
- The H1 is the most important header, logically followed by H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6
- While there should only be ONE H1 per page, there is no limit to H2-H6 headers
- Organize information based on a hierarchy of importance
- Use keywords towards the front of a header
Step 5: Add & Optimize Imagery
As with everything, remember that content should be people-first. That means the imagery you choose should further engage the user with the content on the page. Imagery can also help break up content and create a better user experience, making this one of the many situations in which tenets of SEO bleed into each other. We’ve previously published an entire article on image optimization but the simple steps you need are all here:
- Use professional images (whether you create them, source them, or purchase them, make sure they add an air of professionalism to your site)
- Compress and resize your images before uploading them, this will reduce the work your website needs to do, thus improving your site’s speed
- Give your images descriptive filenames that include relevant keywords (use dashes instead of spaces)
- Use alt text with a keyword (remember, alt text is primarily an accessibility function but you can, and should, also use it as an SEO opportunity by using an image relevant to your core keyword)
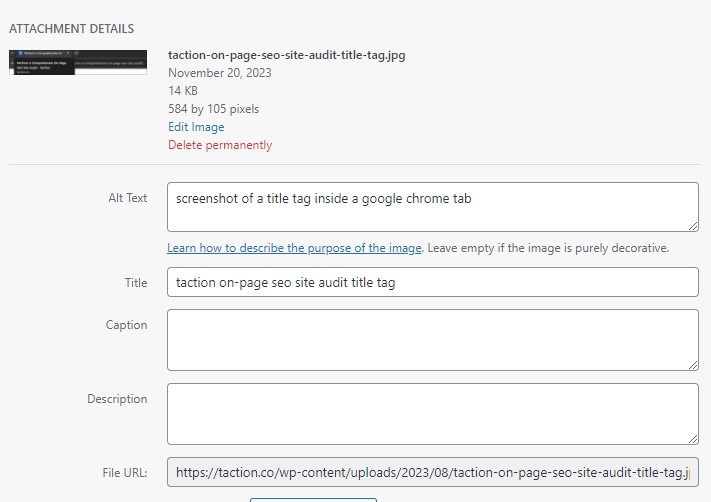
Using WordPress? Every image has an “attachment details” window like the one below. Need to compress an image or change the filename? No need to take it down and start over, use an image optimization plugin and the whole process will be much quicker.
 If you’re wondering video is not mentioned it is mostly due to site speed. Adding video can be great, but videos are large files, even when embedded from YouTube. Oftentimes with SEO, you are going to have to make decisions that go against best practices for the sake of engaging content, branding, accessibility, or maybe even legalities. Try your best to stick to best practices as often as you can – no site is perfect.
If you’re wondering video is not mentioned it is mostly due to site speed. Adding video can be great, but videos are large files, even when embedded from YouTube. Oftentimes with SEO, you are going to have to make decisions that go against best practices for the sake of engaging content, branding, accessibility, or maybe even legalities. Try your best to stick to best practices as often as you can – no site is perfect.
Step 6: Consider the URL
Every page on your site is going to have a unique URL. It is up to you to specify those URL slugs and to incorporate keywords into them. Any CMS you use will automatically generate a URL based on the page title you use, but you can be more specific if you so choose. Keep your URLs short and to the point – most of the time your core keyword will suffice on its own. Make sure to use dashes instead of spaces so that your CMS doesn’t add odd characters or smush the words together.
Step 7: Click-Worthy Meta Descriptions
The only place you’ll see a meta description is in search results. That means you’ve succeeded (to a degree) and it’s your time to shine. While meta descriptions are actually not a ranking factor, the information in a meta description plays a big role in click-through rates, which are a ranking factor. This means that the wording in your meta description isn’t going to get your keyword ranked higher on Google, but if it is written well you will be more likely to get clicks. Those clicks on their own are not a ranking factor, but what happens after the click is arguably the most important piece of the SEO puzzle. Here are the best practices for your meta descriptions followed by an explanation of the click-through conundrum mentioned above.
- Less than 160 characters (or, more specifically, 920 pixels)
- Includes keywords
- Be descriptive: tell them what they’ll see once they click the search result
- Actionable words: tell them how the content on the page will improve their lives
- The meta description for this blog post, as an example:
- Learn how to run a comprehensive site audit of any website’s On-Page SEO. This step-by-step guide offers insights, best practices, SEO tools, and more.
Click Through Conundrum: Are all clicks good?
The click is only good if the search result is good. If each search query is considered a problem, the search results provided by Google should be a solution. If a user sees your webpage in the search results and clicks on it, only to find your webpage is lousy (or, at the very least, doesn’t solve their problem) they will leave the site and probably keep looking for an answer. Google will take note of this. On the other hand, if your webpage gives them the answer they were looking for, causing them to remain on your site and end their search, Google is going to know that webpage is a good search result to use for whatever search query that user typed in. The more often this happens, the higher that webpage will be ranked for the associated search query/keyword.
Step 8: Optimize Links
There are two types of links on every site: internal links and external links. Both are useful in their own way. While sometimes you might use an image or button as a link, more often than not you’ll add a hyperlink to a phrase or keyword. The text of a link is called anchor text. When choosing anchor text you should consider the user experience and target keywords. To consider the user experience means the anchor text should inform the user what the link is for and where it will send them upon clicking it. To consider the target keywords is simply using applicable keywords in your anchor text.
- Internal Links: These are links on your site that lead to other pages on your site. Optimally, your website should create a web of content that naturally links together. Ultimately if a search query leads a user to your site, optimized internal links should bring them to other pages that interest them, answer their questions, or solve their problems.
- External Links: These are links on your site that lead users to another website. Here we start touching upon Off-Page SEO. Linking to pages with high domain authority for relatable keywords, using optimized anchor text, is a great way to build trust with Google. When other domains use external links that send users to your site, that is referred to as a backlink. Backlinks are a top priority of Off-Page SEO strategy.
Page Optimization
Earlier I mentioned that the 6 tenets of SEO work in tandem. Because of that, tasks that fall under Technical SEO, User Experience, or other tenets of SEO can sometimes fall under On-Page SEO as well. These are the highest-priority examples
- Responsive Design. Over half of web traffic is coming from mobile devices. If your website isn’t made using responsive design, you won’t like the results. Even if you are using responsive design, don’t forget to check every page. Sometimes automatic settings of responsive templates don’t look great and require tweaking. Floating navigation menus, embedded videos, and pop-up newsletter signups are among the most common issues you can find when doing a manual overview of your site’s mobile-friendliness.
- Page Speed. People leave slow websites. This matters for 2 reasons. First, because you don’t want people to leave your site before you’ve had the chance to win them over with your fantastic content. Second, because page speed is a confirmed ranking factor by Google. Remember, Google’s primary objective is to give users a positive experience and a slow website does not provide a positive web experience.
- Crawlability. Every website has something called a sitemap. This sitemap is exactly what it sounds like, a map that Google uses to navigate your site. Fortunately, Google provides a free platform called Search Console that allows you to submit a sitemap and have your site crawled. You can also use Search Console to view precious data based on how your site is performing in organic search results. New to Google Properties? No sweat. We’ve created a full step-by-step guide to the Google Properties vital for SEO.
- Connecting Business Profiles. Any business profile that you have should link to your site and be found on your site. That means your Google Business Profile, LinkedIn Company Page, and any other social media account you have. By connecting these official accounts you are creating an aura of trust and professionalism, and confirming with Google which pages are legitimate. Not only that, but you’re giving yourself free backlinks from high-authority sites.
Tools for On-Page SEO
Smart people around the world have made SEO easier than ever with WordPress Plugins, Google Chrome Extensions, Shopify Apps, Auditing Software, and the list goes on. Here is a list of tools that you might find useful for improving your website’s On-Page SEO:
- Semrush. The free version is great for beginners. The pro version is necessary for experts. Semrush has over 55 digital marketing tools, most of which are specifically for SEO purposes. Currently, there are 6 Keyword Research Tools and 3 On-Page SEO Tools. Our suggestion is to create an account, connect your website and Google Properties, then run a site audit and get started on your keyword research while it crawls your site.
- All-in-One SEO. If you’re using WordPress (which we suggest you do), we’ve compiled a list of fantastic WordPress SEO Plugins for you to choose from. AIOSEO is our choice because of its intuitive user experience and comprehensive features. There is a free version with ample features and a pro version that has everything you could need.
- Booster SEO. If you’re using Shopify, there are numerous apps with great SEO features. The Booster SEO is one of the top choices.
- To The Web. Preview your titles, meta descriptions, and more using this easy-to-use web-based tool. Most sites will tell you how many characters are optimal, but TTW will show you exactly what your page will look like in search results based on how many pixels your characters are using.
- SEO Minion. This Chrome & Firefox extension has a plethora of tools built in. Analyze on-page SEO, preview SERPs, check broken links, and more.
- Google Properties. All the Google Properties you need for SEO are free to use. The four in our Google Properties Guide are necessary, while others worth exploring are Google Trends, Google Lighthouse, PageSpeed Insights, and Google Keyword Planner.
Limited Offer
10% off your first 2 months
Sign up for any of our services and receive 10% off your first 2 months. Offer valid for a limited time!